28 Degrees F To C
saludintensiva
Sep 16, 2025 · 5 min read
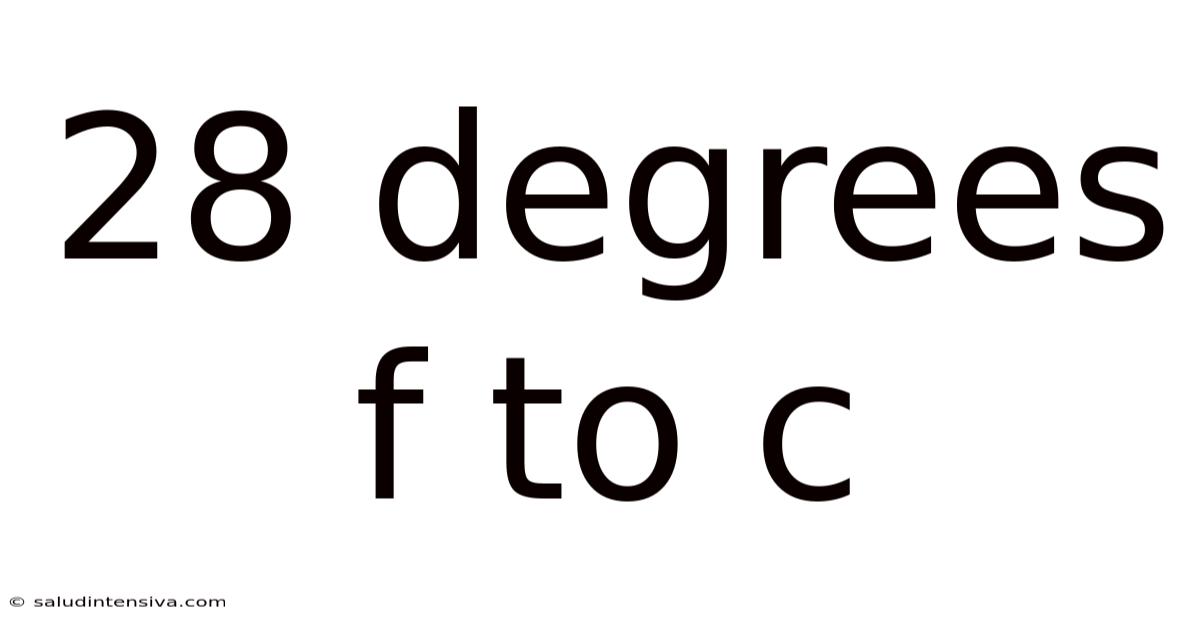
Table of Contents
Converting 28 Degrees Fahrenheit to Celsius: A Comprehensive Guide
Converting temperatures between Fahrenheit (°F) and Celsius (°C) is a common task, particularly for those who work with international data or need to understand weather reports from different parts of the world. This article will comprehensively guide you through the process of converting 28 degrees Fahrenheit to Celsius, explaining the method, the underlying science, and addressing frequently asked questions. We'll also explore the practical implications of this temperature conversion in various contexts.
Introduction: Understanding the Two Scales
Before diving into the conversion, it's crucial to understand the difference between the Fahrenheit and Celsius scales. Both are temperature scales used to measure heat and cold, but they have different origins and reference points.
-
Fahrenheit (°F): This scale was developed by Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit in the early 18th century. It uses the freezing point of water as 32°F and the boiling point of water as 212°F at standard atmospheric pressure.
-
Celsius (°C): Also known as the centigrade scale, Celsius was developed by Anders Celsius in the 18th century. It sets the freezing point of water at 0°C and the boiling point of water at 100°C at standard atmospheric pressure.
The difference in reference points is the key to understanding why the conversion isn't a simple multiplication or division. The scales are related linearly, meaning a consistent relationship exists between them, but an offset is required to account for the differing zero points.
Step-by-Step Conversion: 28°F to °C
The formula to convert Fahrenheit to Celsius is:
°C = (°F - 32) × 5/9
Let's apply this formula to convert 28°F:
-
Subtract 32 from the Fahrenheit temperature: 28°F - 32°F = -4°F
-
Multiply the result by 5/9: -4°F × 5/9 = -2.22°C (approximately)
Therefore, 28 degrees Fahrenheit is approximately -2.22 degrees Celsius.
Detailed Explanation of the Conversion Formula
The formula's components reflect the differences between the Fahrenheit and Celsius scales:
-
(°F - 32): This part accounts for the 32°F difference between the freezing points of water on the two scales. Subtracting 32 aligns the Fahrenheit reading with the Celsius scale's zero point.
-
× 5/9: This fraction accounts for the different size of the degrees on each scale. There are 180 degrees between the freezing and boiling points of water on the Fahrenheit scale (212°F - 32°F = 180°F) and 100 degrees on the Celsius scale. The ratio 5/9 (or 100/180 simplified) adjusts for this difference in degree size.
Practical Applications and Implications of 28°F (-2.22°C)
A temperature of 28°F (-2.22°C) signifies a cold environment. Understanding the implications of this temperature is essential in various contexts:
-
Weather: 28°F indicates cold weather, likely requiring warm clothing. Depending on humidity and wind chill, this temperature could be quite uncomfortable or even dangerous for prolonged exposure.
-
Agriculture: Many plants are sensitive to freezing temperatures. 28°F could cause damage to crops, necessitating protective measures like covering plants or using frost protection methods.
-
Infrastructure: In regions experiencing such temperatures, infrastructure must be designed to withstand freezing conditions. This includes considerations for water pipes, roads, and buildings to prevent damage from freezing water.
-
Human Health: Exposure to 28°F for extended periods without proper protection can lead to hypothermia, a dangerous drop in body temperature.
Scientific Background: Understanding Temperature Measurement
Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles within a substance. Higher temperatures indicate that the particles are moving faster, possessing greater kinetic energy. Both the Fahrenheit and Celsius scales provide a relative measure of this energy, although they use different reference points and degree sizes. The Kelvin scale, an absolute temperature scale, provides a more fundamental measure, where 0 Kelvin represents absolute zero, the theoretical point where all particle motion ceases.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Q: Is there a simpler way to convert Fahrenheit to Celsius?
A: While the formula provided is the most accurate, some calculators and online converters can perform the conversion directly. However, understanding the formula allows for manual calculation and a deeper grasp of the underlying principles.
- Q: What is the difference between a degree Fahrenheit and a degree Celsius?
A: The difference is primarily in the size and reference point. A degree Celsius is larger than a degree Fahrenheit (a 1°C change is equivalent to a 9/5°F change). The reference points – the freezing and boiling points of water – are different on each scale.
- Q: Why are both scales still used today?
A: Both scales have historical significance and continue to be used in different parts of the world. The Fahrenheit scale remains prevalent in some countries, particularly the United States, while the Celsius scale is the standard in most others and the preferred scale in scientific contexts.
- Q: Can I use this formula for temperatures below 0°F?
A: Yes, absolutely. The formula works for any temperature expressed in Fahrenheit. Remember that temperatures below 0°F will result in negative Celsius values.
- Q: What is the equivalent of 28°F in Kelvin?
A: To convert Celsius to Kelvin, you add 273.15. So, -2.22°C + 273.15 = 270.93 Kelvin (approximately).
Conclusion: Mastering Temperature Conversions
Converting 28°F to Celsius, which results in approximately -2.22°C, requires applying the formula (°F - 32) × 5/9. This conversion highlights the differences between the Fahrenheit and Celsius scales and their different reference points and degree sizes. Understanding this conversion is crucial for interpreting temperature data from various sources and appreciating the implications of temperature in various aspects of life, from weather forecasting to agricultural practices and infrastructure design. While a simple calculation, mastering this conversion provides a foundation for further exploration into thermodynamics and other scientific concepts involving temperature measurement. Remember to always double-check your calculations and consider the context of the temperature reading for a complete understanding.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 1 Of 20
Sep 16, 2025
-
Gcf Of 14 And 10
Sep 16, 2025
-
What Are The Multiples 12
Sep 16, 2025
-
7 1 3 Improper Fraction
Sep 16, 2025
-
2 Out Of 13 Percentage
Sep 16, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 28 Degrees F To C . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.