43 C Is What Fahrenheit
saludintensiva
Sep 08, 2025 · 5 min read
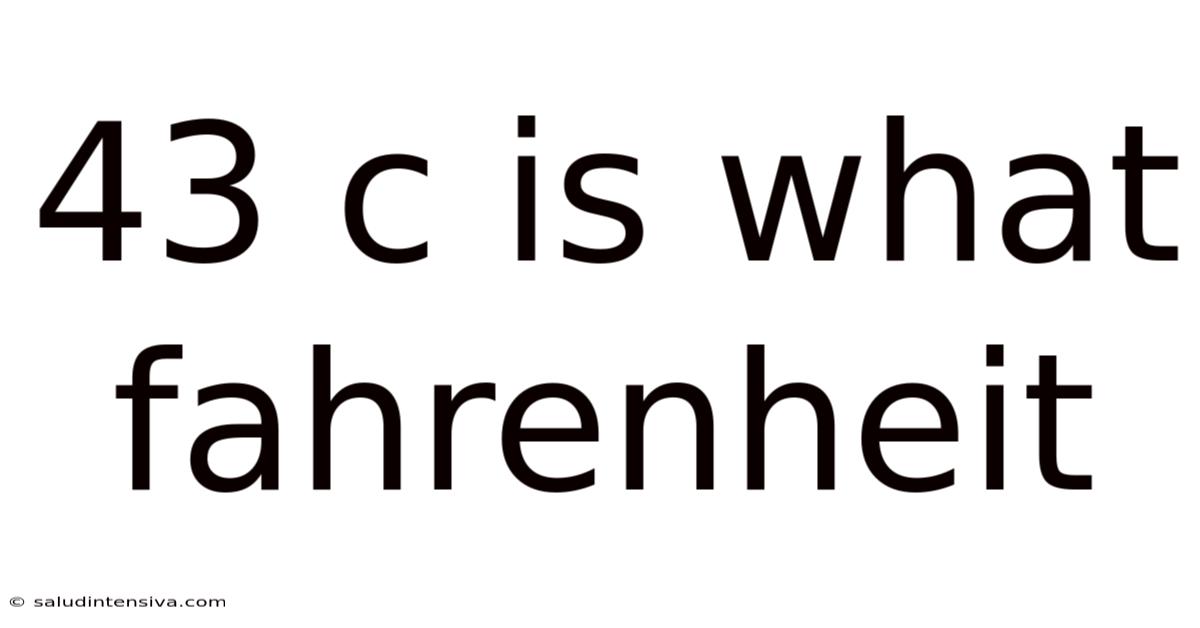
Table of Contents
43°C is What Fahrenheit? Understanding Temperature Conversions
Knowing how to convert between Celsius (°C) and Fahrenheit (°F) is a crucial skill, whether you're checking the weather forecast, baking a cake, or understanding scientific data. This article will comprehensively explain how to convert 43°C to Fahrenheit and delve into the underlying principles of temperature scales, providing a clear and concise understanding for everyone, from students to seasoned professionals. We'll explore the formulas, provide step-by-step calculations, and address frequently asked questions about temperature conversion. By the end, you'll not only know the Fahrenheit equivalent of 43°C but also have a firm grasp of the concepts involved.
Understanding Celsius and Fahrenheit
Before we dive into the conversion, let's briefly understand the two temperature scales:
-
Celsius (°C): A metric unit based on the freezing and boiling points of water at standard atmospheric pressure. Water freezes at 0°C and boils at 100°C. It's widely used globally and is the standard temperature scale in most scientific contexts.
-
Fahrenheit (°F): Primarily used in the United States, its reference points are different from Celsius. Water freezes at 32°F and boils at 212°F.
Converting 43°C to Fahrenheit: The Formula and Calculation
The conversion between Celsius and Fahrenheit is achieved using a simple formula. Here's how to convert 43°C to Fahrenheit:
The Formula:
°F = (°C × 9/5) + 32
Step-by-Step Calculation:
-
Multiply the Celsius temperature by 9/5: 43°C × 9/5 = 77.4°
-
Add 32 to the result: 77.4° + 32° = 109.4°F
Therefore, 43°C is equal to 109.4°F.
A Deeper Dive into the Conversion Formula: Why Does it Work?
The formula (°F = (°C × 9/5) + 32) might seem arbitrary, but it's rooted in the fundamental differences between the Celsius and Fahrenheit scales. Let's break it down:
-
The 9/5 Factor: This ratio represents the difference in the size of the degrees between the two scales. There are 100 degrees between the freezing and boiling points of water in Celsius (0°C to 100°C), and 180 degrees in Fahrenheit (32°F to 212°F). The ratio 180/100 simplifies to 9/5. This factor accounts for the different "size" of a degree in each scale.
-
The +32 Factor: This accounts for the offset between the freezing points of water in the two scales. Water freezes at 0°C but at 32°F. Adding 32 ensures that the conversion accurately reflects this difference.
Practical Applications of Temperature Conversion
Understanding temperature conversions isn't just an academic exercise; it has many real-world applications:
-
Cooking and Baking: Recipes often specify temperatures in either Celsius or Fahrenheit. Accurate conversion is essential for consistent results.
-
Weather Forecasting: Understanding both scales allows for a clearer interpretation of weather reports, especially when traveling internationally.
-
Medicine: Body temperature is often measured in both Celsius and Fahrenheit, requiring accurate conversion for diagnosis and treatment.
-
Science and Engineering: Accurate temperature measurement and conversion are fundamental to scientific experiments, engineering designs, and industrial processes.
-
International Travel: Familiarity with both scales is crucial when traveling to countries that use a different temperature scale.
Beyond the Formula: Understanding Temperature and its Measurement
Temperature is a fundamental physical quantity that measures the average kinetic energy of the particles within a substance. Higher temperatures indicate faster particle movement. The various temperature scales differ primarily in their zero points and the size of their degree increments.
Several other temperature scales exist besides Celsius and Fahrenheit, including:
-
Kelvin (K): An absolute temperature scale where 0 K represents absolute zero, the theoretical point where all molecular motion ceases. Kelvin is widely used in scientific research and is closely related to Celsius (K = °C + 273.15).
-
Rankine (R): An absolute temperature scale based on Fahrenheit. It's less commonly used than Kelvin.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Can I convert Fahrenheit to Celsius?
A1: Absolutely! The reverse formula is: °C = (°F - 32) × 5/9.
Q2: Why are there different temperature scales?
A2: Different scales emerged historically due to different scientific and practical needs. Celsius evolved from a more scientifically rigorous approach, while Fahrenheit developed earlier and was based on different reference points.
Q3: Is it possible to have a negative temperature?
A3: Yes, negative temperatures are possible on Celsius and Fahrenheit scales, indicating temperatures below the freezing point of water. However, negative temperatures on the Kelvin scale are not possible.
Q4: Are there online converters for temperature?
A4: Yes, many websites and apps offer convenient online temperature converters that instantly perform Celsius to Fahrenheit and vice-versa conversions. These are helpful for quick calculations.
Q5: What are some common temperature equivalents to remember?
A5: Knowing a few common equivalents can be helpful: 0°C = 32°F (freezing point of water), 100°C = 212°F (boiling point of water), 20°C ≈ 68°F (room temperature), 37°C = 98.6°F (normal human body temperature).
Conclusion: Mastering Temperature Conversions
Understanding temperature conversions is a valuable skill that transcends simple arithmetic. It's a fundamental concept with applications across various fields. By grasping the formula, its underlying rationale, and the significance of different temperature scales, you'll be equipped to confidently navigate the world of temperature measurement and conversion. Remember the formula: °F = (°C × 9/5) + 32, and you'll be well-prepared to tackle any Celsius to Fahrenheit conversion, starting with our initial example of 43°C being equivalent to 109.4°F. This knowledge will prove invaluable in your daily life and studies. Beyond just calculating 43°C to Fahrenheit, we hope this in-depth guide has broadened your understanding of temperature scales and their practical importance.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
10 5 In Simplest Form
Sep 09, 2025
-
90 Degrees F To C
Sep 09, 2025
-
25 6 As A Decimal
Sep 09, 2025
-
What Are Multiples Of 13
Sep 09, 2025
-
55 Celsius Is What Fahrenheit
Sep 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 43 C Is What Fahrenheit . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.