40 Trillion / 80 Million
saludintensiva
Sep 15, 2025 · 5 min read
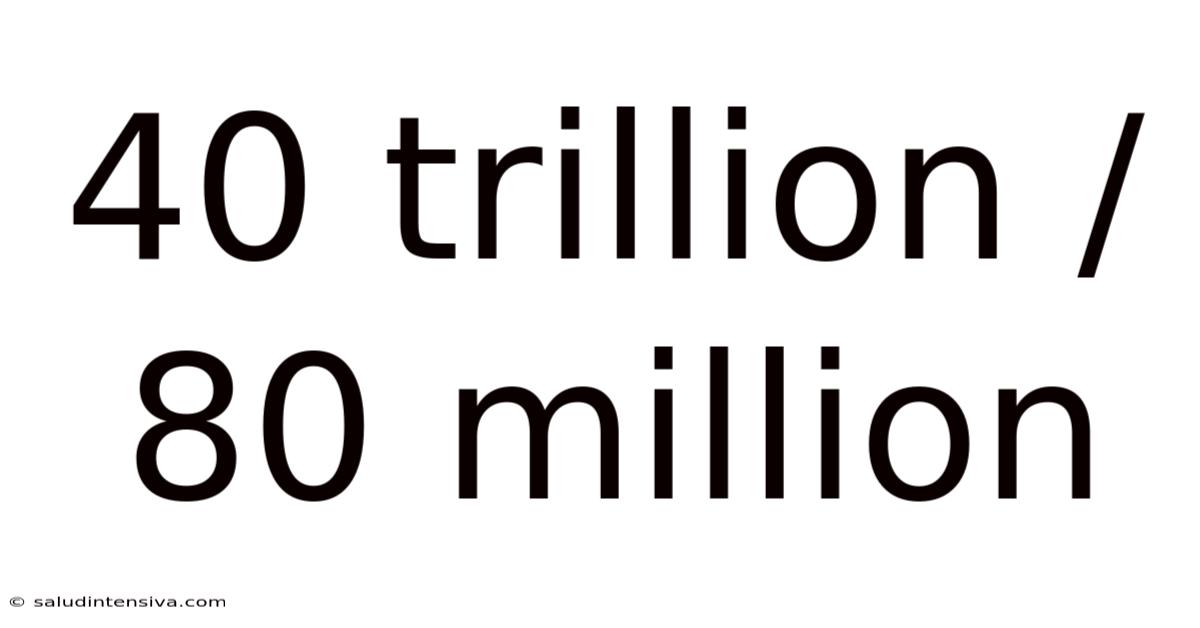
Table of Contents
Decoding the Immense: Understanding 40 Trillion Divided by 80 Million
This article delves into the seemingly complex calculation of 40 trillion divided by 80 million, exploring the mathematical process, its real-world implications, and how to approach similar large-number problems. We'll unpack the solution step-by-step, making it accessible even for those who aren't math enthusiasts. Understanding this calculation can be surprisingly useful in comprehending large-scale data analysis, financial projections, and even scientific discoveries. Let's dive in!
Understanding the Numbers: Trillions and Millions
Before tackling the division, let's briefly understand the magnitude of the numbers involved. Trillion and million are both large numbers representing powers of ten. One million (1,000,000) is 10<sup>6</sup>, meaning 1 followed by six zeros. One trillion (1,000,000,000,000) is 10<sup>12</sup>, or 1 followed by twelve zeros. This means a trillion is one million times one million (1,000,000 x 1,000,000 = 1,000,000,000,000). Grasping this difference in scale is crucial to understanding the result of our calculation.
The Mathematical Process: Step-by-Step Solution
Now, let's perform the division: 40 trillion / 80 million. To make this easier, let's express the numbers in scientific notation:
- 40 trillion = 40 x 10<sup>12</sup> = 4 x 10<sup>13</sup>
- 80 million = 80 x 10<sup>6</sup> = 8 x 10<sup>7</sup>
Therefore, the calculation becomes: (4 x 10<sup>13</sup>) / (8 x 10<sup>7</sup>)
We can break this down further:
-
Divide the coefficients: 4 / 8 = 0.5
-
Divide the powers of 10: 10<sup>13</sup> / 10<sup>7</sup> = 10<sup>(13-7)</sup> = 10<sup>6</sup>
-
Combine the results: 0.5 x 10<sup>6</sup>
This result can be expressed in standard notation as 500,000 or five hundred thousand.
Therefore, 40 trillion divided by 80 million equals 500,000.
Real-World Applications: Interpreting the Result
The result of 500,000 has diverse applications depending on the context. Let's imagine a few scenarios:
-
National Debt: If a nation has a debt of 40 trillion and its population is 80 million, each citizen would hypothetically owe 500,000 in debt. Of course, this is a simplified model; real-world debt distribution is far more complex.
-
Resource Allocation: If a country has 40 trillion units of a natural resource (e.g., barrels of oil) and needs to distribute it evenly among 80 million citizens, each citizen would receive 500,000 units.
-
Economic Indicators: In macroeconomic analysis, this calculation could represent the average wealth per capita, the average income per household, or even the average energy consumption per individual. It’s a powerful tool for understanding large-scale economic trends.
-
Scientific Data: In fields like astronomy or particle physics, dealing with extremely large numbers is common. This type of calculation could represent the average number of particles per unit volume or the average distance between celestial bodies. The implications would depend heavily on the specific context of the research.
The key takeaway is that the 500,000 result provides a crucial average or per capita value, but this average may not accurately reflect the distribution in the real world. Some individuals or entities might possess significantly more or less than the average. This highlights the importance of careful interpretation and consideration of potential inequalities when working with large-scale data.
Handling Larger Numbers: Practical Tips and Techniques
Working with numbers as large as trillions and millions can seem daunting, but a few strategies can simplify the process:
-
Scientific Notation: Expressing numbers in scientific notation (e.g., 4 x 10<sup>13</sup>) makes large-number calculations significantly easier, especially when dealing with multiplication and division.
-
Unit Conversion: Pay close attention to units. Ensure you're working with consistent units throughout the calculation to avoid errors.
-
Approximation: When dealing with extremely large numbers, especially in estimations, rounding numbers to the nearest power of 10 can simplify calculations significantly while maintaining a reasonable level of accuracy.
-
Spreadsheets and Calculators: For more complex scenarios or larger datasets, spreadsheets like Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets, or specialized scientific calculators, offer powerful tools for handling these calculations with ease. They reduce the risk of manual errors.
-
Breaking Down the Problem: When faced with a complex calculation involving large numbers, breaking it down into smaller, more manageable steps can significantly improve clarity and reduce the chance of errors. This is exactly the approach we took in our step-by-step solution.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What if the numbers were different? How would the process change?
A1: The process remains the same. You would simply substitute the new numbers into the division formula, express them in scientific notation if needed, divide the coefficients, divide the powers of 10, and then combine the results.
Q2: Are there any potential errors when dealing with such large numbers?
A2: Yes, manual calculations can be prone to errors, especially when dealing with many digits. Using scientific notation, calculators, or spreadsheets can help mitigate this risk significantly. Also, rounding errors can occur when approximating large numbers.
Q3: What if I don't understand scientific notation?
A3: Scientific notation is a way of representing very large or very small numbers concisely. For example, 40 trillion (40,000,000,000,000) is written as 4 x 10<sup>13</sup>. The exponent (13) represents the number of places you move the decimal point to the left to get 4.
Conclusion: Mastering Large-Number Calculations
Understanding how to handle calculations involving large numbers like trillions and millions is a valuable skill applicable across many fields. By using techniques like scientific notation, breaking down complex problems, and utilizing tools like spreadsheets, these calculations become manageable and provide meaningful insights. The seemingly daunting division of 40 trillion by 80 million ultimately simplifies to a manageable 500,000, highlighting the power of breaking down complex problems into smaller, easier-to-handle components. This understanding not only equips you to tackle similar mathematical challenges but also enhances your ability to interpret large-scale data and its implications in various contexts. Remember to always consider the context and potential limitations of averages when interpreting such results.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Multiples Of 2 And 5
Sep 15, 2025
-
3 14 As A Decimal
Sep 15, 2025
-
16 9 As A Mixed Number
Sep 15, 2025
-
3 10 As A Decimal
Sep 15, 2025
-
1 3 8 6 8
Sep 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 40 Trillion / 80 Million . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.