3 Divided By 4 9
saludintensiva
Sep 16, 2025 · 5 min read
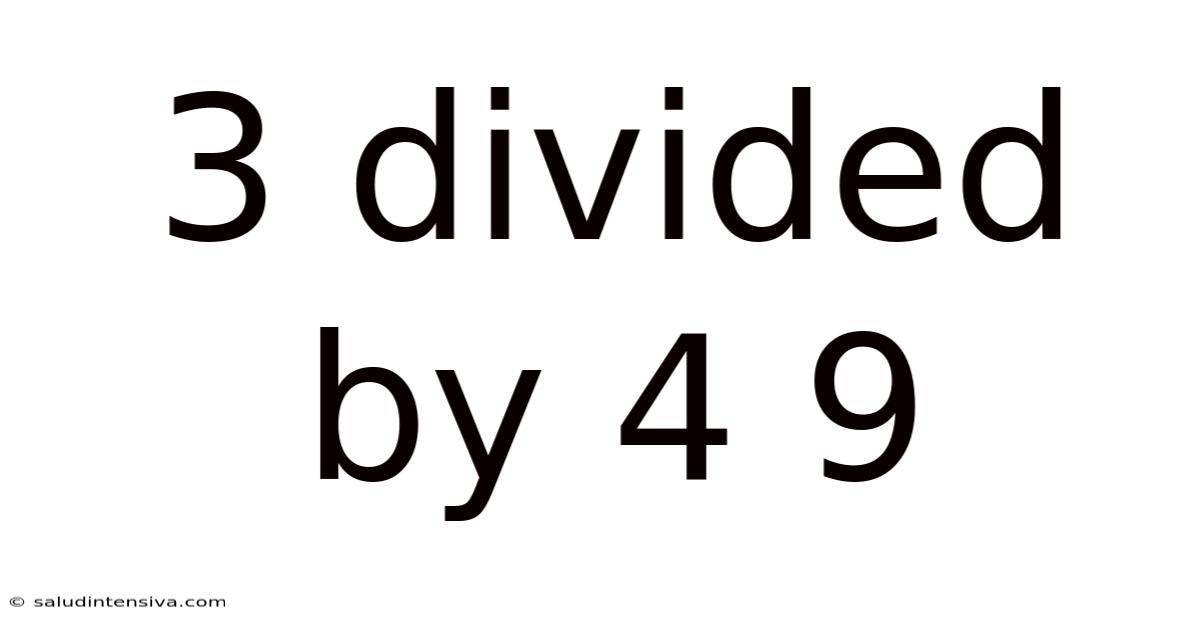
Table of Contents
Decoding 3 Divided by 49: A Deep Dive into Division and its Applications
This article explores the seemingly simple calculation of 3 divided by 49, delving beyond the immediate answer to illuminate the underlying principles of division, its various applications, and the broader mathematical concepts it connects to. Understanding this seemingly basic operation provides a solid foundation for tackling more complex mathematical problems. We will cover the calculation itself, explore different methods of solving it, discuss its relevance in real-world scenarios, and address common questions and misconceptions surrounding division. By the end, you’ll have a much deeper appreciation for the power and elegance of this fundamental arithmetic operation.
Understanding Division: A Foundational Concept
Division is one of the four basic arithmetic operations, alongside addition, subtraction, and multiplication. It essentially represents the process of sharing or partitioning a quantity into equal parts. When we say "3 divided by 49," we are asking: "If we have 3 units, how many times can we take away groups of 49 units?" Since we cannot take away any full groups of 49 from 3, we expect the result to be a fraction or decimal less than 1.
Key Terminology:
- Dividend: The number being divided (in this case, 3).
- Divisor: The number by which we are dividing (in this case, 49).
- Quotient: The result of the division (the answer).
- Remainder: The amount left over after dividing (if any). In this instance, we anticipate a remainder because the dividend is smaller than the divisor.
Calculating 3 Divided by 49: Methods and Approaches
There are several ways to calculate 3 divided by 49. Let’s explore a few:
1. Long Division: This traditional method provides a step-by-step approach. Since 3 is smaller than 49, we can add a decimal point and zeros to the dividend to continue the division:
0.0612...
49 | 3.0000
-0
30
-0
300
-294
60
-49
110
-98
12
The long division shows that 3 divided by 49 is approximately 0.0612... The ellipsis (...) indicates that the decimal continues infinitely without repeating, meaning it’s an irrational number.
2. Fraction Representation: Division can be represented as a fraction: 3 ÷ 49 = 3/49. This fraction is already in its simplest form, as 3 and 49 have no common factors other than 1. This is a precise representation, avoiding the approximation inherent in decimal form.
3. Using a Calculator: The simplest method is using a calculator. Inputting "3 ÷ 49" will directly give you the decimal approximation (approximately 0.06122448979...).
4. Understanding the Decimal: The decimal representation (approximately 0.0612) signifies that for every 49 units, we have approximately 0.0612 units of the original 3 units. This highlights the proportional relationship between the dividend and divisor.
Real-World Applications of Division: Beyond the Classroom
While the specific calculation of 3 divided by 49 might seem abstract, the principle of division underlies numerous real-world applications:
-
Resource Allocation: Imagine dividing 3 liters of paint amongst 49 rooms for touch-ups. The calculation (3 ÷ 49) will determine how much paint is allocated to each room.
-
Financial Calculations: Dividing profits amongst shareholders, calculating unit costs of products based on total production cost and quantity, or determining the portion of a monthly budget allocated to specific expenses all involve division.
-
Recipe Scaling: Reducing the ingredients in a recipe often requires dividing the quantities. For example, if a recipe calls for 49 grams of flour, and you want to make only a third of the recipe, you would divide 49 by 3.
-
Rate and Speed Calculations: Determining average speed by dividing distance traveled by time taken uses the principles of division. Similarly, calculating the unit rate (price per item) requires division.
-
Data Analysis: In statistics, many calculations involve dividing totals by the number of data points to calculate averages or means.
-
Physics and Engineering: Division is crucial in solving equations relating to velocity, acceleration, force, and other physical quantities.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Related Mathematical Concepts
The simple division of 3 by 49 opens doors to exploring more advanced mathematical concepts:
-
Fractions and Decimals: The conversion between fractions (3/49) and decimals (approximately 0.0612) reinforces the relationship between these two representations of numbers.
-
Rational and Irrational Numbers: While the fraction 3/49 is a rational number (a number expressible as a fraction of two integers), its decimal representation is an irrational number because it extends infinitely without repeating.
-
Limits and Approximations: The decimal representation is an approximation. Understanding the concept of limits in calculus allows us to explore how this approximation approaches the true value.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Why is the result of 3 divided by 49 a decimal and not a whole number?
A: The result is a decimal because the dividend (3) is smaller than the divisor (49). This means we cannot divide 3 into equal groups of 49 without resulting in a fraction or decimal.
Q: How accurate is the decimal approximation?
A: The accuracy depends on how many decimal places are calculated. The more decimal places, the more accurate the approximation, but it will always be an approximation because the decimal representation is non-terminating and non-repeating.
Q: Is there a remainder in this division?
A: While the long division process seems to yield a remainder in each step, there is no true remainder in the sense of a whole number. The remainder continues infinitely as indicated by the non-terminating decimal.
Q: What if I needed a more precise answer than the decimal approximation provides?
A: In cases where high precision is needed, using the fractional representation (3/49) is superior, as it provides the exact value without approximation.
Conclusion: The Significance of a Simple Calculation
While the calculation of 3 divided by 49 might seem insignificant on its own, it serves as a powerful illustration of fundamental mathematical concepts. Understanding the process, different solution methods, and its applications reinforces the importance of division as a building block for more complex calculations and problem-solving in various fields. The journey from a simple calculation to a deeper understanding of mathematical principles highlights the beauty and practicality of even the most basic arithmetic operations. Remember, every mathematical concept, however simple it may initially appear, opens a world of possibilities and opportunities for deeper exploration and understanding.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Gcf Of 60 And 90
Sep 16, 2025
-
7 4 As A Decimal
Sep 16, 2025
-
What Is 200db Hy Depreciation
Sep 16, 2025
-
33 Percent As A Fraction
Sep 16, 2025
-
Gcf Of 80 And 100
Sep 16, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 3 Divided By 4 9 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.